Trench Technology
Reliable and Time-Tested Wastewater Distribution
Trench systems are one of the most common and dependable onsite wastewater distribution methods used in Missouri. These systems direct effluent from the septic tank into absorption trenches, where natural soil processes complete the treatment.
Depending on site conditions, a variety of trench materials and configurations can be used to meet health, safety, and environmental standards.
Types of Trench Systems
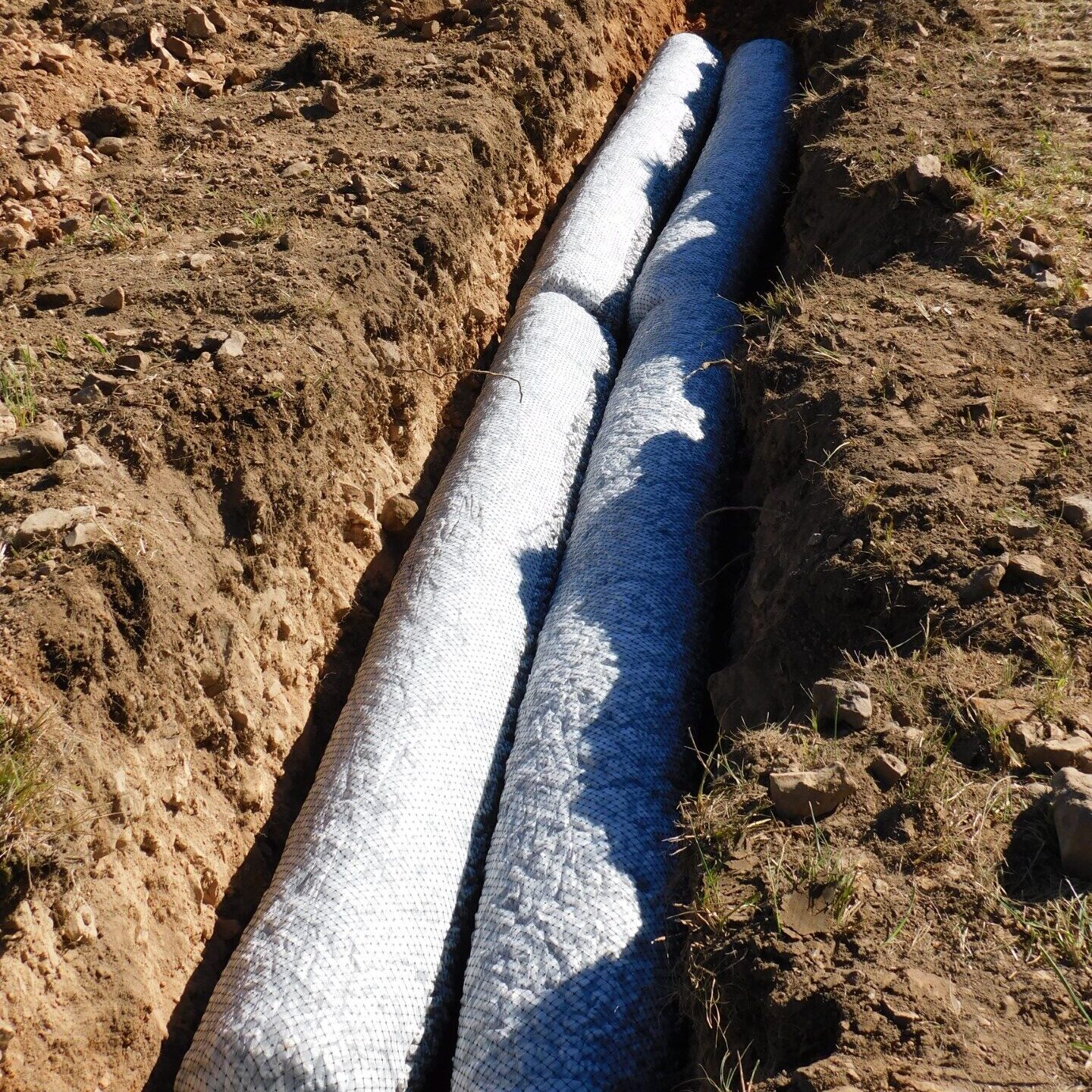
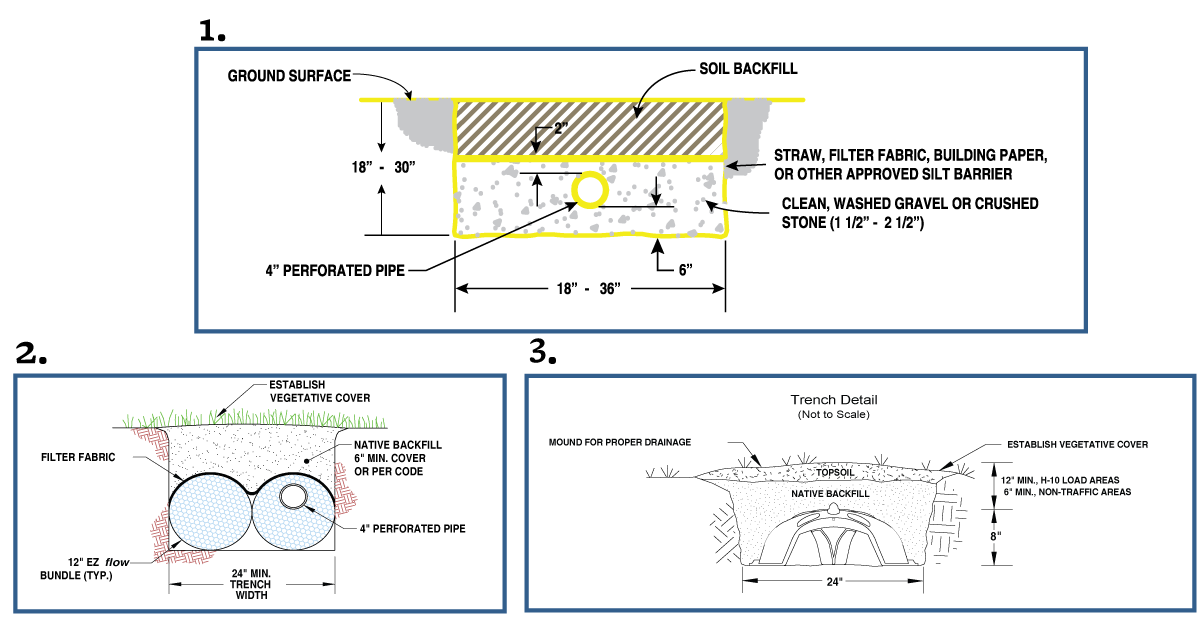
Pipe and Gravel
A traditional method that uses perforated pipes surrounded by gravel to distribute wastewater.
Trenches are typically 18"–24" deep
May be installed as shallow as 12" with additional cover soil
Effluent exits through the perforated pipe, percolates through gravel, and enters the soil for final treatment
Polystyrene Aggregate Bundles
These pre-packaged bundles use recycled materials and simplify installation.
Trenches are typically 18"–24" deep
May be installed as shallow as 12" with additional cover soil
Effluent exits through the perforated pipe, percolates through gravel, and enters the soil for final treatment
Leaching Chambers
A traditional method that uses perforated pipes surrounded by gravel to distribute wastewater.
Solid pipe transports effluent from the septic tank to open-bottomed chambers
Effluent is absorbed by the soil through the chamber floor and vented side slots
Often made from recycled content
Why Maintenance Matters
Proper care of your trench system is essential to:
Protect groundwater and local drinking water sources
Prevent exposure to serious pathogens like hepatitis A, salmonella, or giardia
Reduce nutrient pollution from nitrogen and phosphorus
Avoid costly system failure, replacements can run from $4,500 to $30,000
Regular inspections, pumping every 2–5 years, and keeping detailed service records all go a long way toward extending the system’s life.
Do’s of System Care
- Obtain permits before repairs or construction
- Hire licensed and certified installers
- Make tanks accessible with secure risers and lids
Conserve water to avoid overloading - Keep stormwater and roof runoff away from the system
- Use cleaning products in moderation and dispose of hazardous waste properly
Don’ts of System Use
- Never enter a septic tank, toxic gases are fatal
- Don’t drive or park vehicles over trenches
- Avoid planting trees or shrubs near the system
- Don’t pour grease, solvents, or harsh chemicals down drains
- Don’t flush non-biodegradable items like wipes, diapers, or feminine hygiene products
- Skip enzyme or yeast additives, they don’t help and may harm your system
Have Questions?
Contact Missouri Smallflows Organization for support or questions. contact@mosmallflows.org
(417) 631-4027



